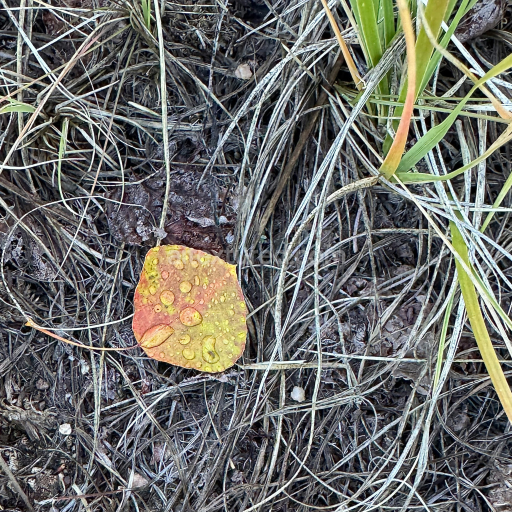
This seamless 3D texture pack features photorealistic renditions of various Minecraft foliage blocks, including oak, birch, spruce, jungle, acacia, and dark oak leaves, alongside grass_top and mycelium surfaces. The base materials are primarily organic plant matter and soil substrates, rendered with a detailed leaf vein structure and natural ground cover elements. Each leaf texture captures the thin, fibrous cellulose matrix typical of deciduous and coniferous leaves, combined with subtle variations in moisture content and surface roughness that influence light absorption and scattering. The grass_top and mycelium textures reflect densely packed, fine organic fibers and fungal hyphae networks, respectively, layered atop a porous soil or decomposed organic matter substrate. The overall geometric form is a finely veined, irregular tessellation mimicking leaf patterns and soil granularity, maintaining Minecraft’s characteristic pixelated block style while enhancing realism through 3D detail.
Compositionally, the texture’s substrate represents a fibrous plant cuticle reinforced by lignin polymers, providing structural rigidity and slight translucency in leaf sections. Binders are implied through the cellular matrix holding the fibers together, while aggregates consist of chloroplast granules and microscopic stomatal openings that contribute to subtle surface irregularities. The grass_top and mycelium textures introduce additional granularity and fine particulate matter, simulating soil minerals and fungal spores embedded within the organic layer. Porosity varies across the textures, with leaves showing minimal surface porosity but evident micro-relief from veins and edges, whereas mycelium and podzol exhibit higher porosity with rough, uneven surfaces. Surface finish ranges from matte to softly reflective, with light scattering enhanced by microfacet structures, captured in the roughness and normal maps.
These materials are meticulously mapped to PBR channels to maximize realism and compatibility. The BaseColor (Albedo) maps display natural pigments from chlorophyll-rich greens to muted browns and grays, accurately reflecting seasonal and biome variations. Normal maps encode the intricate vein networks and subtle surface undulations, providing depth and tactile realism. Roughness maps vary to simulate waxy leaf coatings or the drier, textured soil and fungal surfaces, while metallic maps remain near zero, consistent with non-metallic organic matter. Ambient Occlusion maps enhance shadowing in crevices and overlapping leaves, and Height/Displacement maps enable precise surface relief for parallax or tessellation effects. The entire pack is rendered in ultra-high 8K resolution, ensuring sharp detail and scalability for close-up renders and large-scale scenes.
Designed for seamless tiling and optimized for use in Blender, Unreal Engine, and Unity, these textures allow creators to build richly detailed natural environments with minimal performance overhead. For best results, it is advisable to adjust the UV scale to maintain the pixelated Minecraft aesthetic while leveraging the high-resolution detail. Additionally, fine-tuning roughness values can help balance between subtle leaf glossiness and the matte finish of ground covers. Blending height and normal maps can further enhance depth perception, especially when using parallax occlusion mapping or tessellation shaders. This nuanced control over material properties ensures a versatile and realistic texturing solution for both game development and 3D visualization projects.
How to Use These Seamless PBR Textures in Blender
This guide shows how to connect a full PBR texture set to Principled BSDF in Blender (Cycles or Eevee). Works with any of our seamless textures free download, including PBR PNG materials for Blender / Unreal / Unity.
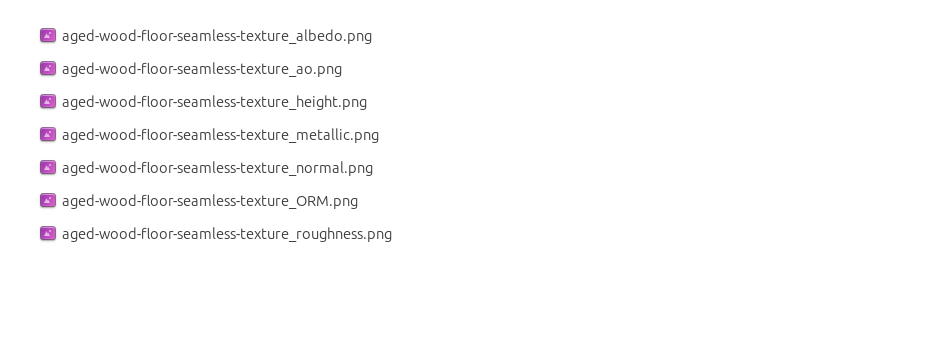
What’s inside the download
*_albedo.png — Base Color (sRGB)*_normal.png — Normal map (Non-Color)*_roughness.png — Roughness (Non-Color)*_metallic.png — Metallic (Non-Color)*_ao.png — Ambient Occlusion (Non-Color)*_height.png — Height / Displacement (Non-Color)*_ORM.png — Packed map (R=AO, G=Roughness, B=Metallic, Non-Color)
Quick start (Node Wrangler, 30 seconds)
- Enable the addon: Edit → Preferences → Add-ons → Node Wrangler.
- Create a material and select the Principled BSDF node.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + T and select the maps
albedo, normal, roughness, metallic (skip height and ORM for now) → Open.
The addon wires Base Color, Normal (with a Normal Map node), Roughness, and Metallic automatically.
- Add AO and Height using the “Manual wiring” steps below (5 and 6).
Manual wiring (full control)
- Create a material (Material Properties → New) and open the Shader Editor.
- Add an Image Texture node for each map. Set Color Space:
- Albedo → sRGB
- AO, Roughness, Metallic, Normal, Height, ORM → Non-Color
- Connect to Principled BSDF:
albedo → Base Colorroughness → Roughnessmetallic → Metallic (for wood this often stays near 0)normal → Normal Map node (Type: Tangent Space) → Normal of Principled.
If details look “inverted”, enable Invert Y on the Normal Map node.
- Ambient Occlusion (AO):
- Add a MixRGB (or Mix Color) node in mode Multiply.
- Input A =
albedo, Input B = ao, Factor = 1.0.
- Output of Mix → Base Color of Principled (replaces the direct albedo connection).
- Height / Displacement:
Cycles — true displacement
- Material Properties → Settings → Displacement: Displacement and Bump.
- Add a Displacement node: connect
height → Height, set Midlevel = 0.5, Scale = 0.02–0.08 (tune to taste).
- Output of Displacement → Material Output → Displacement.
- Add geometry density (e.g., Subdivision Surface) so displacement has polygons to work with.
Eevee (or lightweight Cycles) — bump only
- Add a Bump node:
height → Height.
- Set Strength = 0.2–0.5, Distance = 0.05–0.1, and connect Normal output to Principled’s Normal.
Using the packed ORM texture (optional)
Instead of separate AO/Roughness/Metallic maps you can use the single *_ORM.png:
- Add one Image Texture (Non-Color) → Separate RGB (or Separate Color).
- R (red) → AO (use it in the Multiply node with albedo as above).
- G (green) → Roughness of Principled.
- B (blue) → Metallic of Principled.
UVs & seamless tiling
- These textures are seamless. If your mesh has no UVs, go to UV Editing → Smart UV Project.
- For scale/repeat, add Texture Coordinate (UV) → Mapping and plug it into all texture nodes.
Increase Mapping → Scale (e.g., 2/2/2) to tile more densely.
Recommended starter values
- Normal Map Strength: 0.5–1.0
- Bump Strength: ~0.3
- Displacement Scale (Cycles): ~0.03
Common pitfalls
- Wrong Color Space (normals/roughness/etc. must be Non-Color).
- “Inverted” details → enable Invert Y on the Normal Map node.
- Over-strong relief → lower Displacement Scale or Bump Strength.
Example: Download Wood Textures and instantly apply parquet or rustic planks inside Blender for architectural visualization.
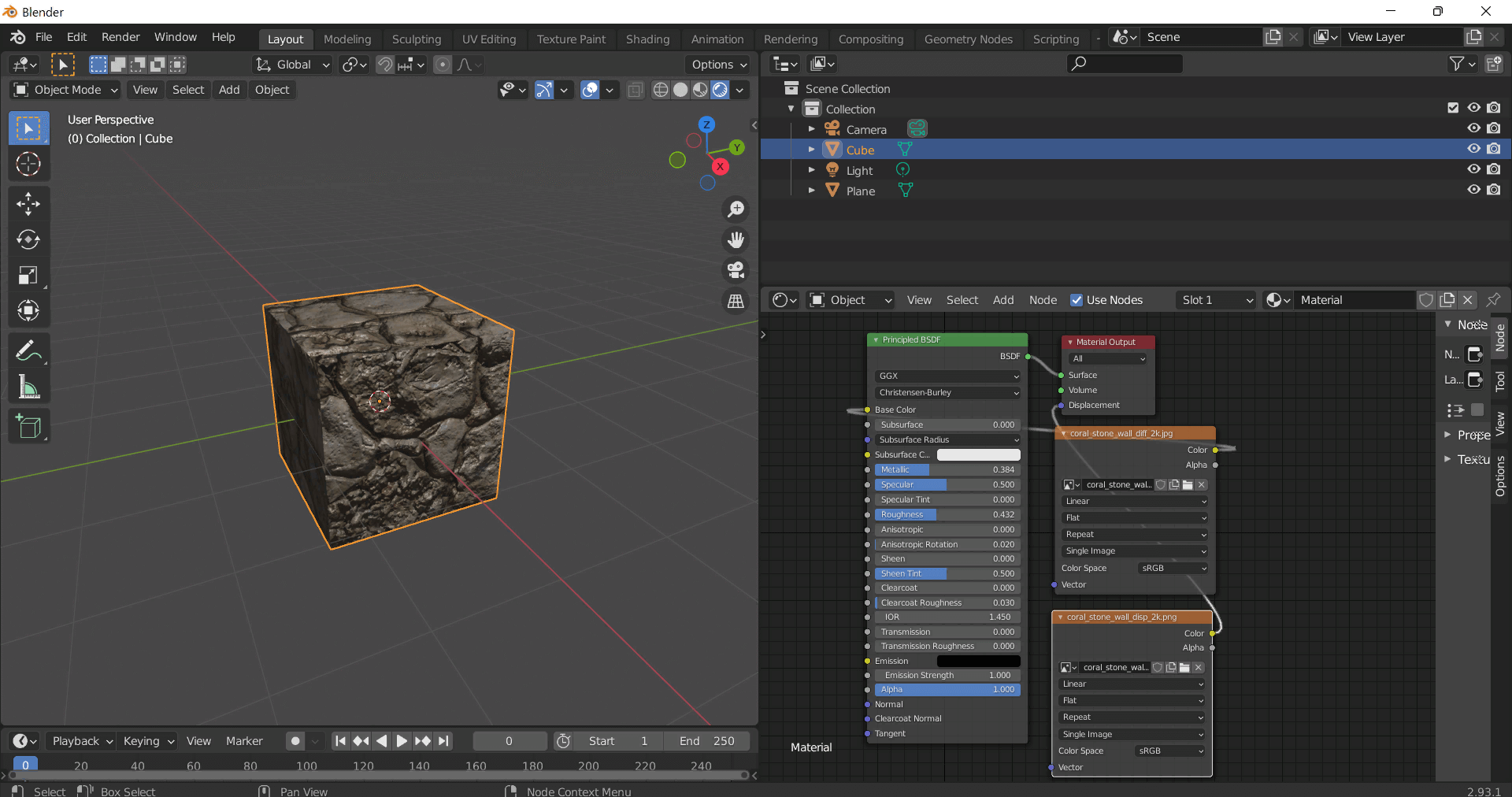
To add the downloaded texture, go to Add — Texture — Image Texture.
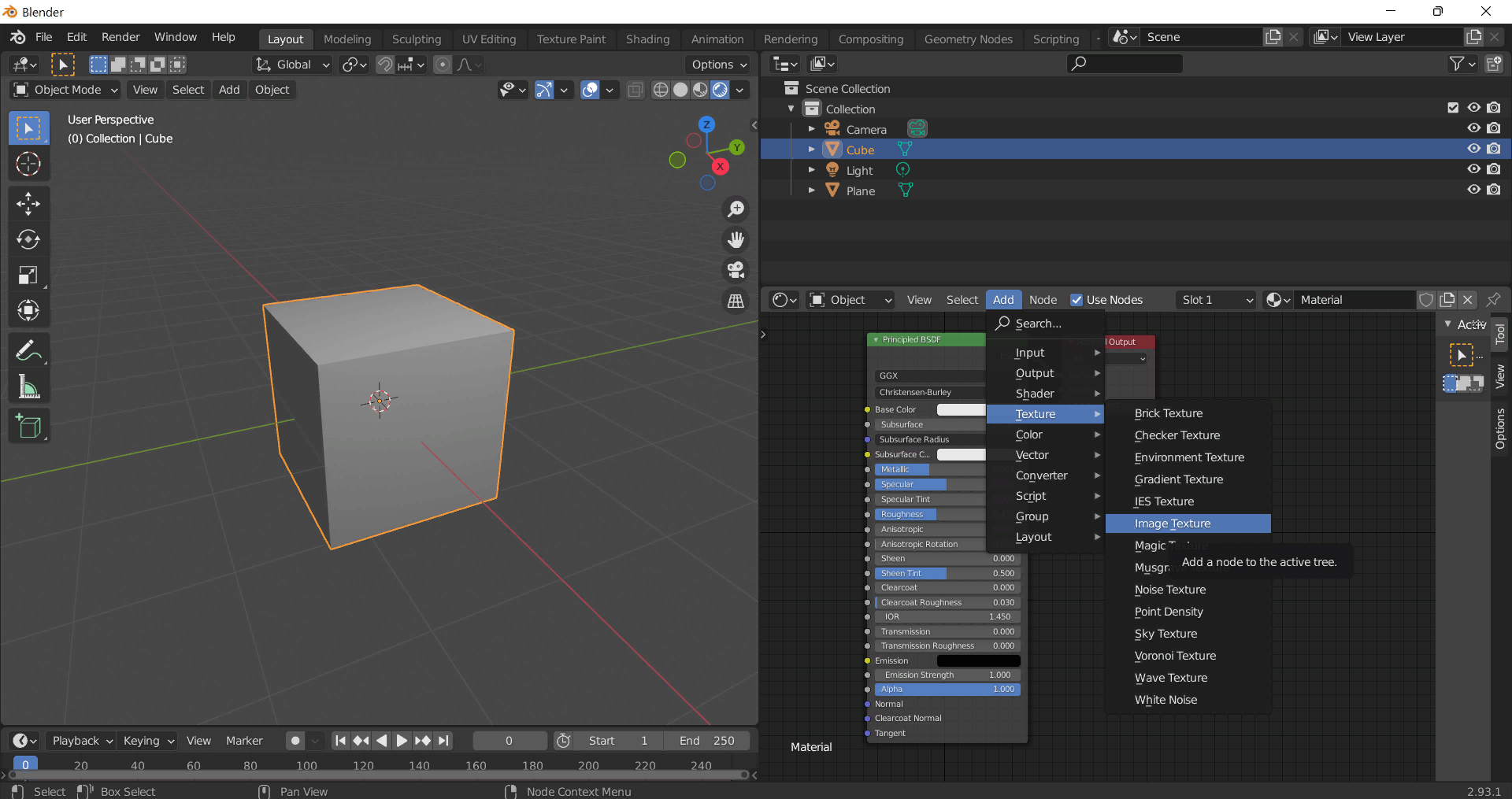
Add a node and click the Open button.
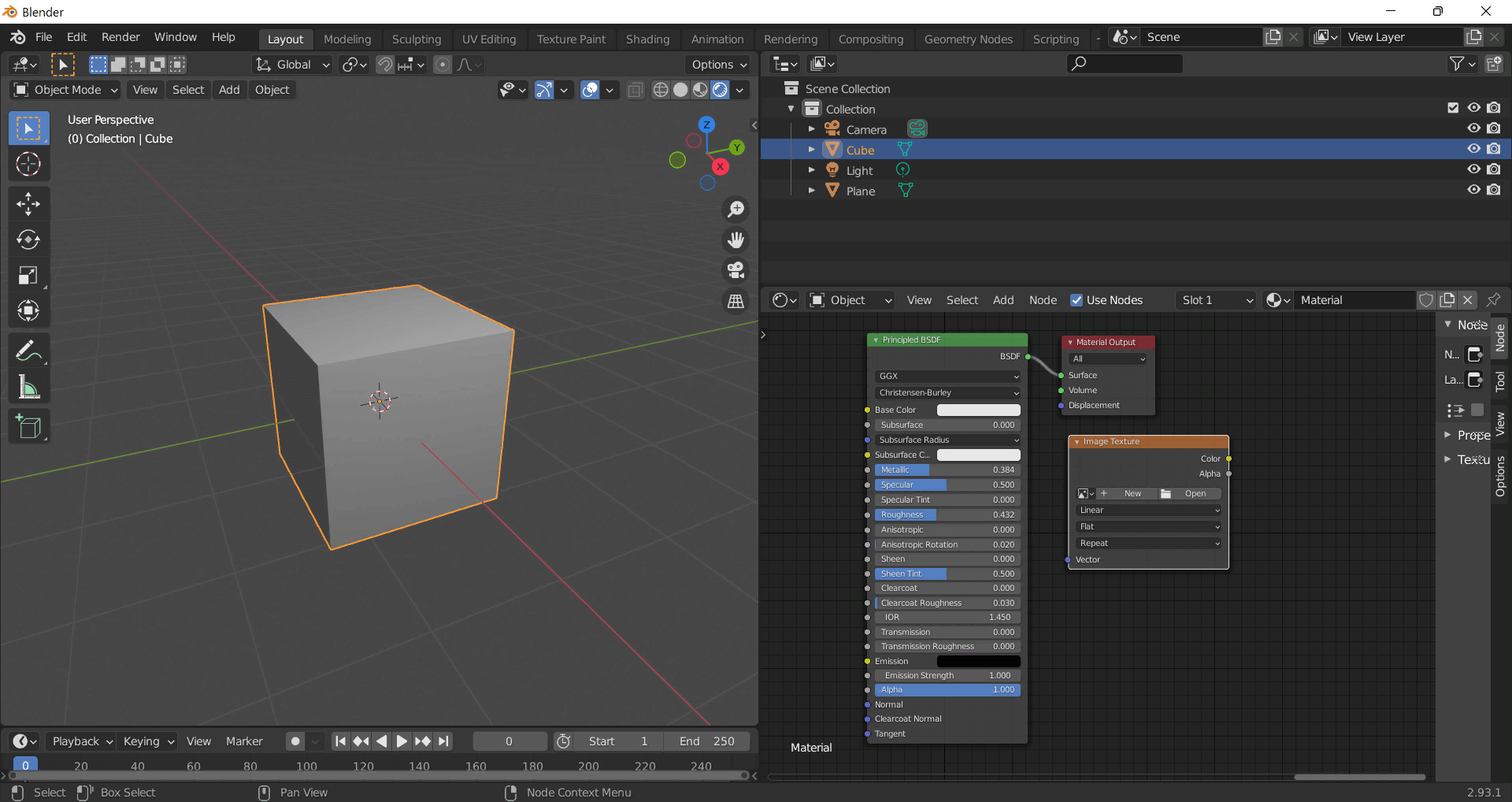
Select the required texture on your hard drive and connect Color to Base Color.