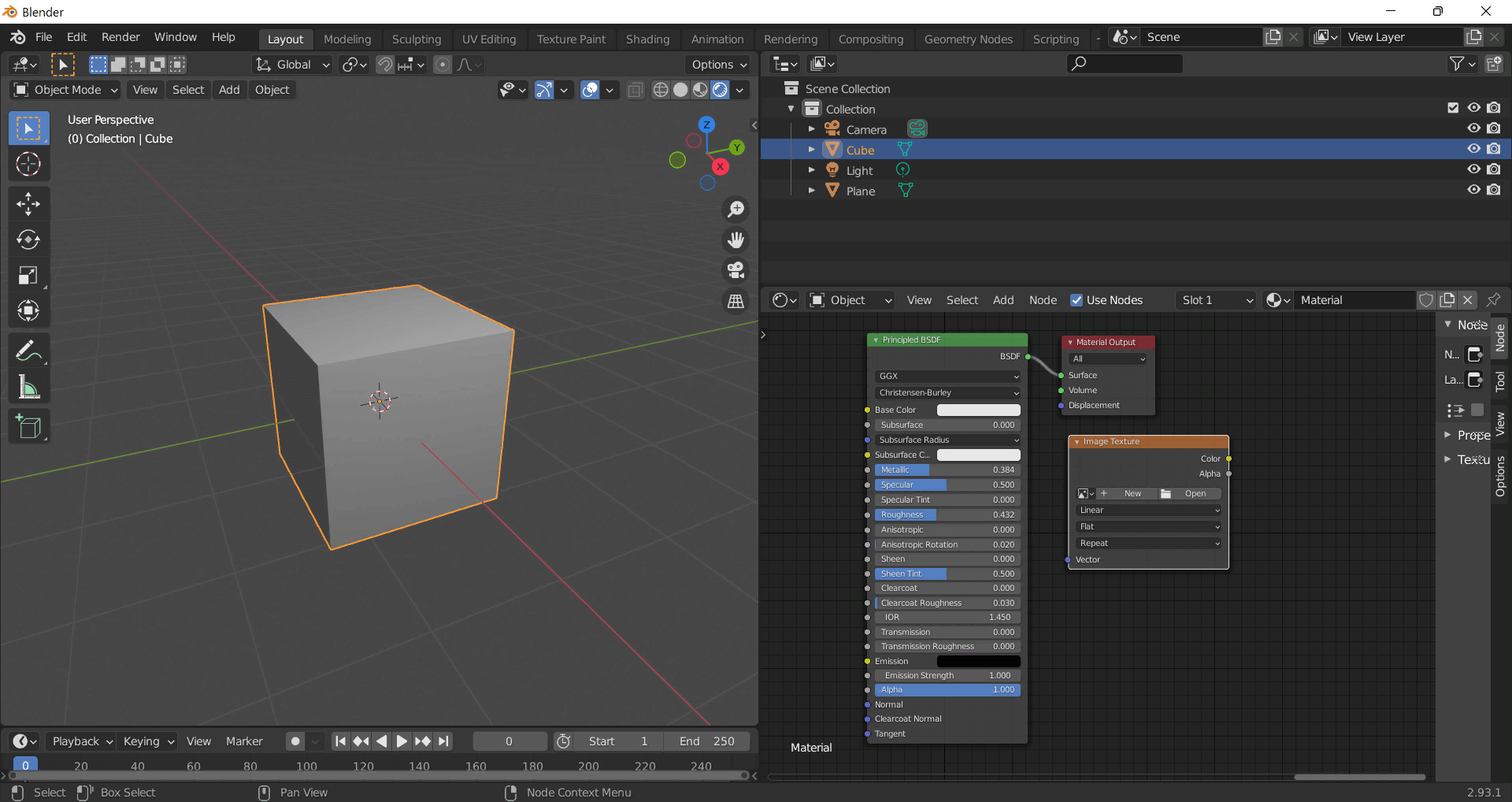
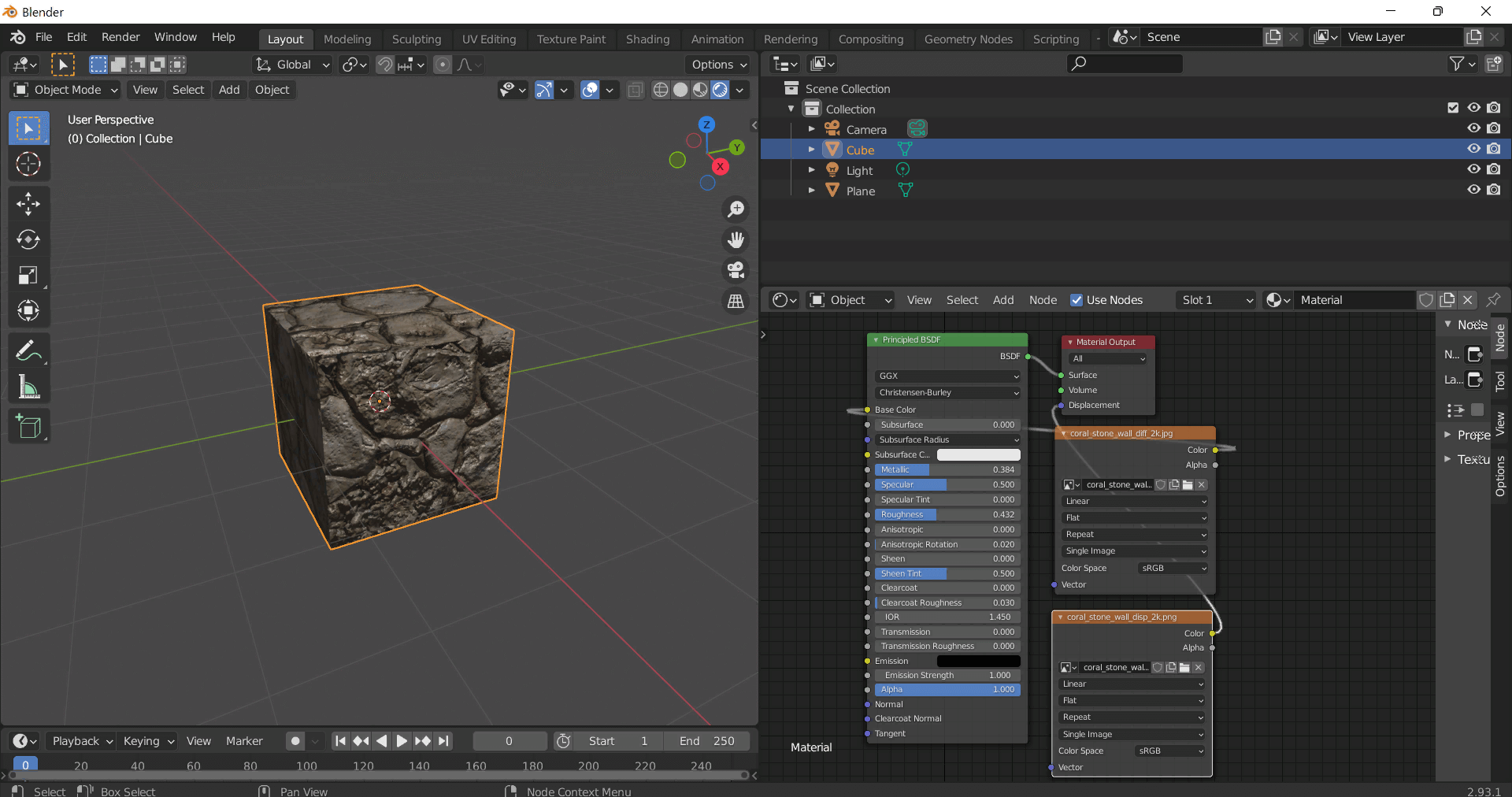
How to Use These Seamless PBR Textures in Blender
This guide shows how to connect a full PBR texture set to Principled BSDF in Blender (Cycles or Eevee). Works with any of our seamless textures free download, including PBR PNG materials for Blender / Unreal / Unity.
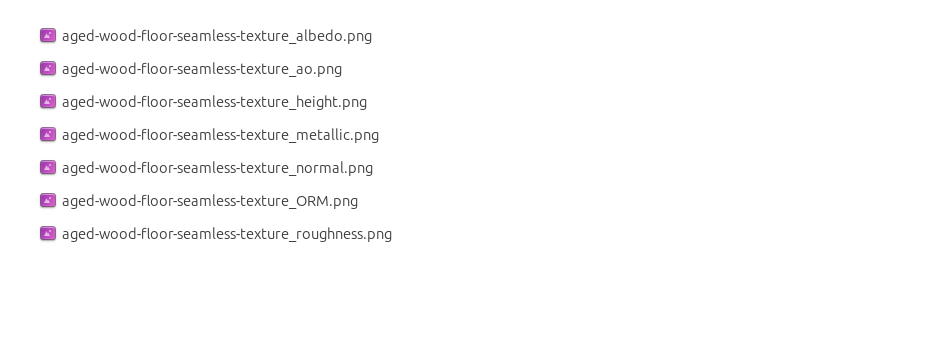
What’s inside the download
*_albedo.png— Base Color (sRGB)*_normal.png— Normal map (Non-Color)*_roughness.png— Roughness (Non-Color)*_metallic.png— Metallic (Non-Color)*_ao.png— Ambient Occlusion (Non-Color)*_height.png— Height / Displacement (Non-Color)*_ORM.png— Packed map (R=AO, G=Roughness, B=Metallic, Non-Color)
Quick start (Node Wrangler, 30 seconds)
- Enable the addon: Edit → Preferences → Add-ons → Node Wrangler.
- Create a material and select the Principled BSDF node.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + T and select the maps albedo, normal, roughness, metallic (skip height and ORM for now) → Open. The addon wires Base Color, Normal (with a Normal Map node), Roughness, and Metallic automatically.
- Add AO and Height using the “Manual wiring” steps below (5 and 6).
Manual wiring (full control)
- Create a material (Material Properties → New) and open the Shader Editor.
- Add an Image Texture node for each map. Set Color Space:
- Albedo → sRGB
- AO, Roughness, Metallic, Normal, Height, ORM → Non-Color
- Connect to Principled BSDF:
albedo→ Base Colorroughness→ Roughnessmetallic→ Metallic (for wood this often stays near 0)normal→ Normal Map node (Type: Tangent Space) → Normal of Principled. If details look “inverted”, enable Invert Y on the Normal Map node.
- Ambient Occlusion (AO):
- Add a MixRGB (or Mix Color) node in mode Multiply.
- Input A =
albedo, Input B =ao, Factor = 1.0. - Output of Mix → Base Color of Principled (replaces the direct albedo connection).
- Height / Displacement:
Cycles — true displacement
- Material Properties → Settings → Displacement: Displacement and Bump.
- Add a Displacement node: connect
height→ Height, set Midlevel = 0.5, Scale = 0.02–0.08 (tune to taste). - Output of Displacement → Material Output → Displacement.
- Add geometry density (e.g., Subdivision Surface) so displacement has polygons to work with.
Eevee (or lightweight Cycles) — bump only
- Add a Bump node:
height→ Height. - Set Strength = 0.2–0.5, Distance = 0.05–0.1, and connect Normal output to Principled’s Normal.
Using the packed ORM texture (optional)
Instead of separate AO/Roughness/Metallic maps you can use the single *_ORM.png:
- Add one Image Texture (Non-Color) → Separate RGB (or Separate Color).
- R (red) → AO (use it in the Multiply node with albedo as above).
- G (green) → Roughness of Principled.
- B (blue) → Metallic of Principled.
UVs & seamless tiling
- These textures are seamless. If your mesh has no UVs, go to UV Editing → Smart UV Project.
- For scale/repeat, add Texture Coordinate (UV) → Mapping and plug it into all texture nodes. Increase Mapping → Scale (e.g., 2/2/2) to tile more densely.
Recommended starter values
- Normal Map Strength: 0.5–1.0
- Bump Strength: ~0.3
- Displacement Scale (Cycles): ~0.03
Common pitfalls
- Wrong Color Space (normals/roughness/etc. must be Non-Color).
- “Inverted” details → enable Invert Y on the Normal Map node.
- Over-strong relief → lower Displacement Scale or Bump Strength.
Example: Download Wood Textures and instantly apply parquet or rustic planks inside Blender for architectural visualization.
To add the downloaded texture, go to Add — Texture — Image Texture.
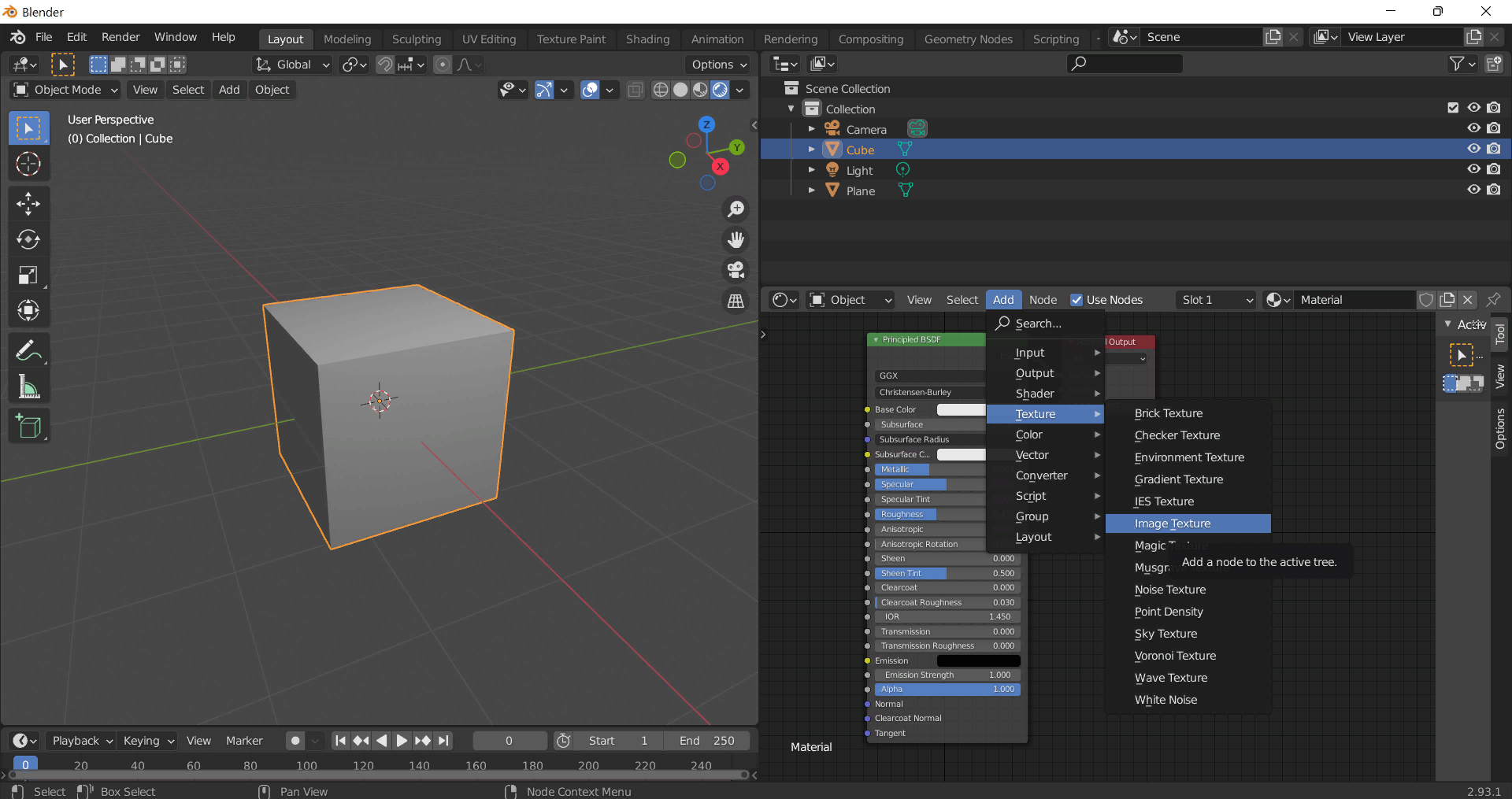
Add a node and click the Open button.