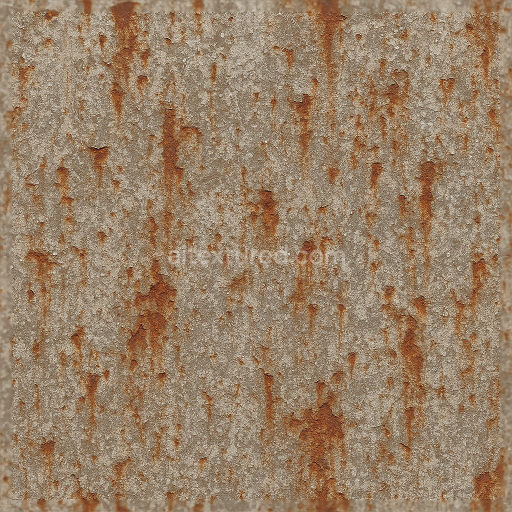
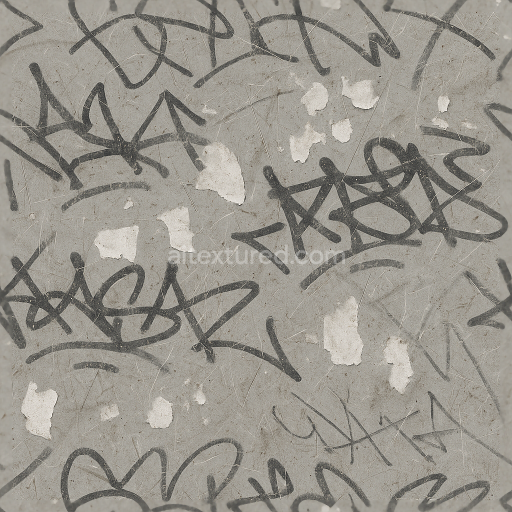
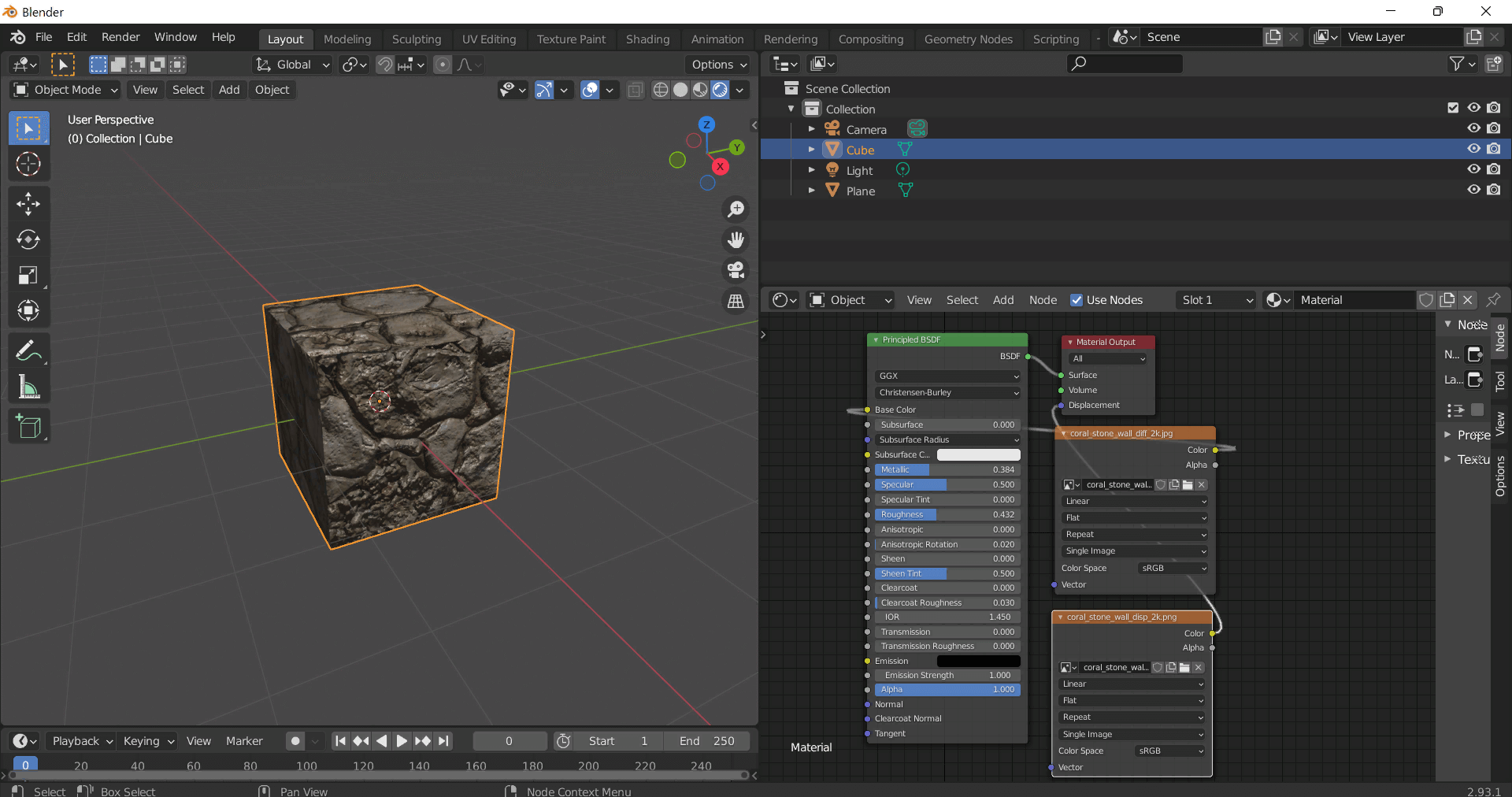
This seamless 3D PBR texture rendered at an impressive 8K resolution combines the tactile qualities of worn leather and distressed fabric with intricate surface details that evoke a strong sense of age and use. The primary substrate features a tightly woven fabric base interlaced with fibrous threads that have been pulled and frayed creating natural inconsistencies in the textile weave. Overlaying this is a layer of weathered leather characterized by its cracked and creased surface exhibiting varied porosity due to prolonged exposure and wear. The leather’s finish is matte to semi-glossy reflecting a subtle sheen where oils and natural wear have smoothed the surface while deeper creases retain a rough tactile grain. Colorants within the leather and fabric layers show muted earth tones—faded browns and grays—accentuated by irregular fabric stains that suggest accumulated dirt and moisture exposure over time.
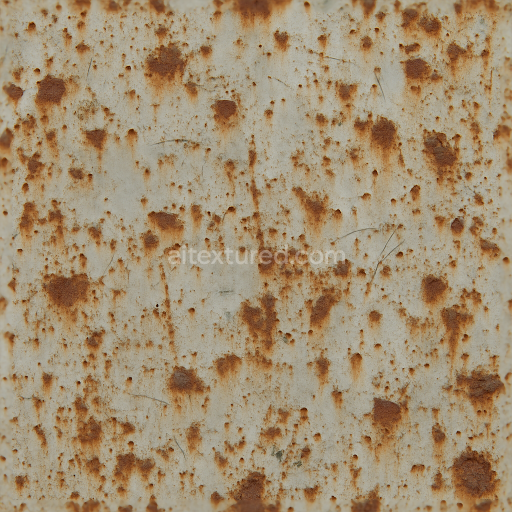
Complementing the organic materials the texture integrates elements of aged industrial metal including rusted chains and metal panels exhibiting dents paint chips and surface rust. These metallic sections feature oxidized finishes with uneven corrosion patterns where the rust’s reddish-brown hues contrast with peeling chipped paint revealing the underlying metal substrate. The metal’s roughness varies significantly: smoother dented areas retain a faint metallic luster while rusted patches are highly matte and porous indicating advanced surface degradation. The paint chips expose subtle layers of primer and bare metal enhancing the material complexity. This mixed-material composition creates a layered heterogeneous surface that reflects a realistic interaction between textile leather and corroded metal elements.
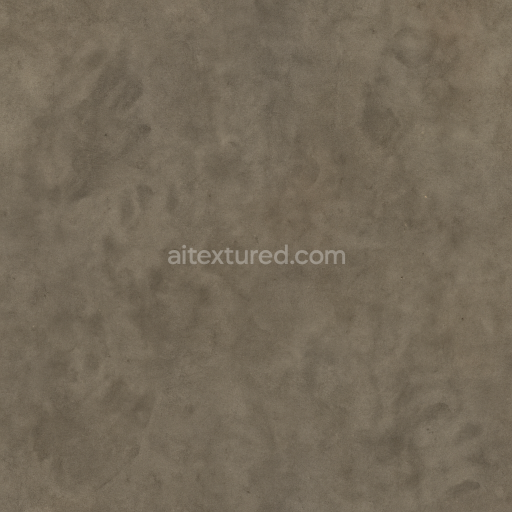
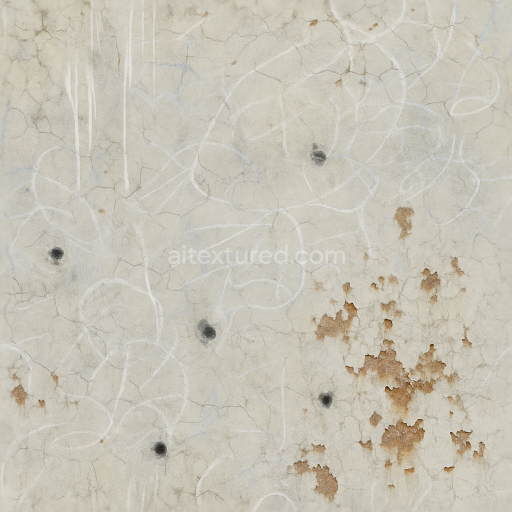
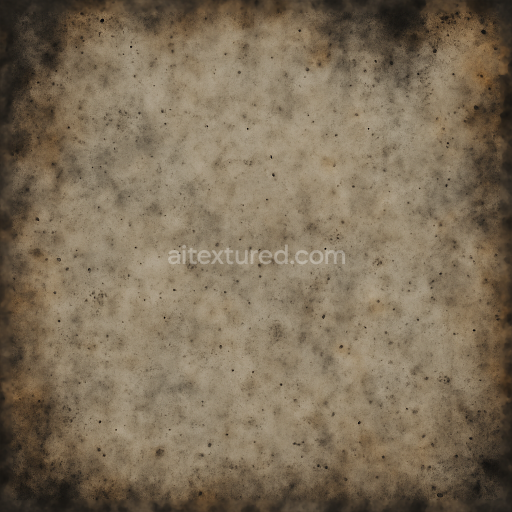
From a PBR workflow perspective the BaseColor (Albedo) channel captures the nuanced color variations of the leather’s faded browns the stained fabric’s muted grays and beiges and the rusted metal’s warm oranges and reds all devoid of lighting information for accurate shading. The Normal map encodes fine surface details such as thread pulls leather grain wrinkles metal dents and paint chip edges contributing to pronounced relief in 3D renders. Roughness values range broadly with the smoother worn leather and metal dents exhibiting lower roughness while the fabric stains and rusted surfaces show higher roughness for diffuse reflection. The Metallic channel isolates metal components marking rusted chains and metal dents as fully metallic while leather and fabric remain non-metallic. Ambient Occlusion enhances shadowing within creases thread gaps and dented metal areas providing depth. Height or Displacement maps reinforce the physical depth of thread pulls leather cracks and chipped paint supporting parallax effects and more realistic silhouettes.
This texture is fully optimized for use in Blender Unreal Engine and Unity ensuring compatibility and high fidelity across multiple 3D platforms. For best results it is recommended to carefully adjust UV scaling to maintain the delicate balance between visible fabric fibers and leather grain without pixelation. Additionally fine-tuning roughness values can help blend the tactile transitions between soft fabric and hard metal surfaces. When implementing displacement or parallax mapping blending with the normal map is advised to preserve subtle surface details while enhancing overall depth perception. This makes the texture ideal for detailed props aged clothing upholstery or industrial-themed assets requiring a realistic portrayal of mixed material wear and degradation.
How to Use These Seamless PBR Textures in Blender
This guide shows how to connect a full PBR texture set to Principled BSDF in Blender (Cycles or Eevee). Works with any of our seamless textures free download, including PBR PNG materials for Blender / Unreal / Unity.
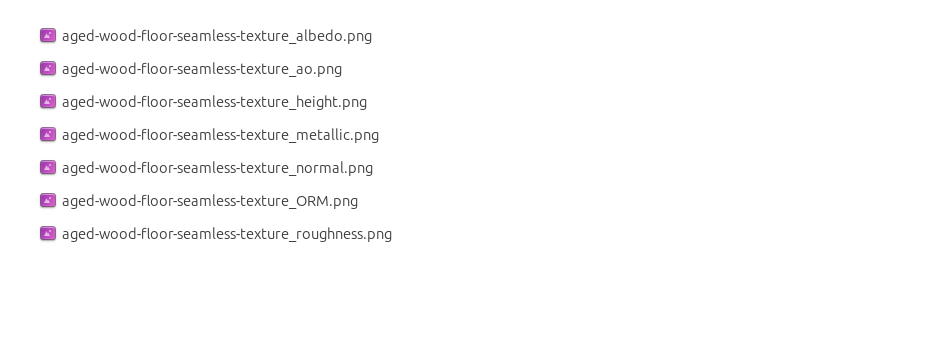
What’s inside the download
*_albedo.png — Base Color (sRGB)*_normal.png — Normal map (Non-Color)*_roughness.png — Roughness (Non-Color)*_metallic.png — Metallic (Non-Color)*_ao.png — Ambient Occlusion (Non-Color)*_height.png — Height / Displacement (Non-Color)*_ORM.png — Packed map (R=AO, G=Roughness, B=Metallic, Non-Color)
Quick start (Node Wrangler, 30 seconds)
- Enable the addon: Edit → Preferences → Add-ons → Node Wrangler.
- Create a material and select the Principled BSDF node.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + T and select the maps
albedo, normal, roughness, metallic (skip height and ORM for now) → Open.
The addon wires Base Color, Normal (with a Normal Map node), Roughness, and Metallic automatically.
- Add AO and Height using the “Manual wiring” steps below (5 and 6).
Manual wiring (full control)
- Create a material (Material Properties → New) and open the Shader Editor.
- Add an Image Texture node for each map. Set Color Space:
- Albedo → sRGB
- AO, Roughness, Metallic, Normal, Height, ORM → Non-Color
- Connect to Principled BSDF:
albedo → Base Colorroughness → Roughnessmetallic → Metallic (for wood this often stays near 0)normal → Normal Map node (Type: Tangent Space) → Normal of Principled.
If details look “inverted”, enable Invert Y on the Normal Map node.
- Ambient Occlusion (AO):
- Add a MixRGB (or Mix Color) node in mode Multiply.
- Input A =
albedo, Input B = ao, Factor = 1.0.
- Output of Mix → Base Color of Principled (replaces the direct albedo connection).
- Height / Displacement:
Cycles — true displacement
- Material Properties → Settings → Displacement: Displacement and Bump.
- Add a Displacement node: connect
height → Height, set Midlevel = 0.5, Scale = 0.02–0.08 (tune to taste).
- Output of Displacement → Material Output → Displacement.
- Add geometry density (e.g., Subdivision Surface) so displacement has polygons to work with.
Eevee (or lightweight Cycles) — bump only
- Add a Bump node:
height → Height.
- Set Strength = 0.2–0.5, Distance = 0.05–0.1, and connect Normal output to Principled’s Normal.
Using the packed ORM texture (optional)
Instead of separate AO/Roughness/Metallic maps you can use the single *_ORM.png:
- Add one Image Texture (Non-Color) → Separate RGB (or Separate Color).
- R (red) → AO (use it in the Multiply node with albedo as above).
- G (green) → Roughness of Principled.
- B (blue) → Metallic of Principled.
UVs & seamless tiling
- These textures are seamless. If your mesh has no UVs, go to UV Editing → Smart UV Project.
- For scale/repeat, add Texture Coordinate (UV) → Mapping and plug it into all texture nodes.
Increase Mapping → Scale (e.g., 2/2/2) to tile more densely.
Recommended starter values
- Normal Map Strength: 0.5–1.0
- Bump Strength: ~0.3
- Displacement Scale (Cycles): ~0.03
Common pitfalls
- Wrong Color Space (normals/roughness/etc. must be Non-Color).
- “Inverted” details → enable Invert Y on the Normal Map node.
- Over-strong relief → lower Displacement Scale or Bump Strength.
Example: Download Wood Textures and instantly apply parquet or rustic planks inside Blender for architectural visualization.
To add the downloaded texture, go to Add — Texture — Image Texture.
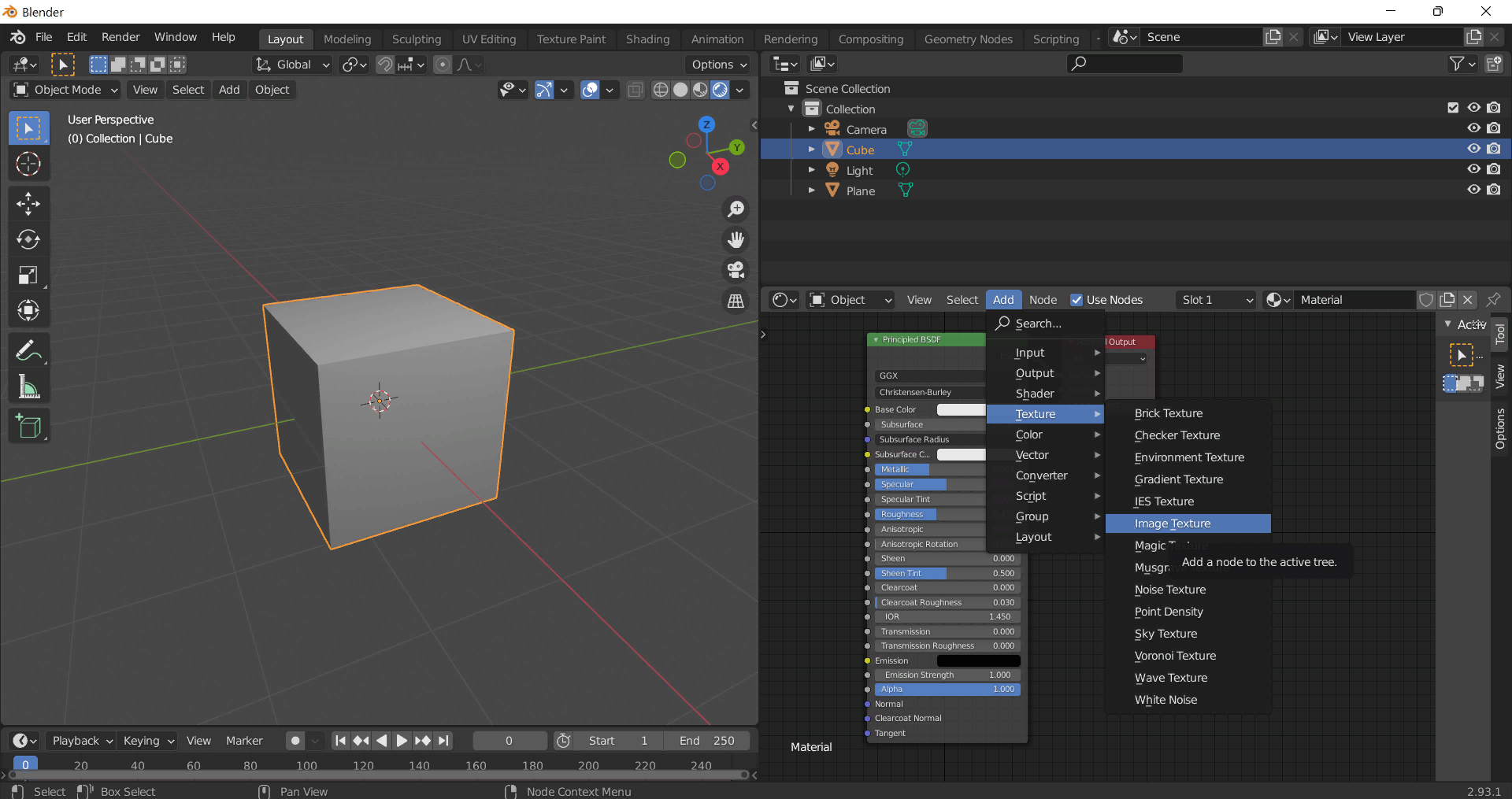
Add a node and click the Open button.
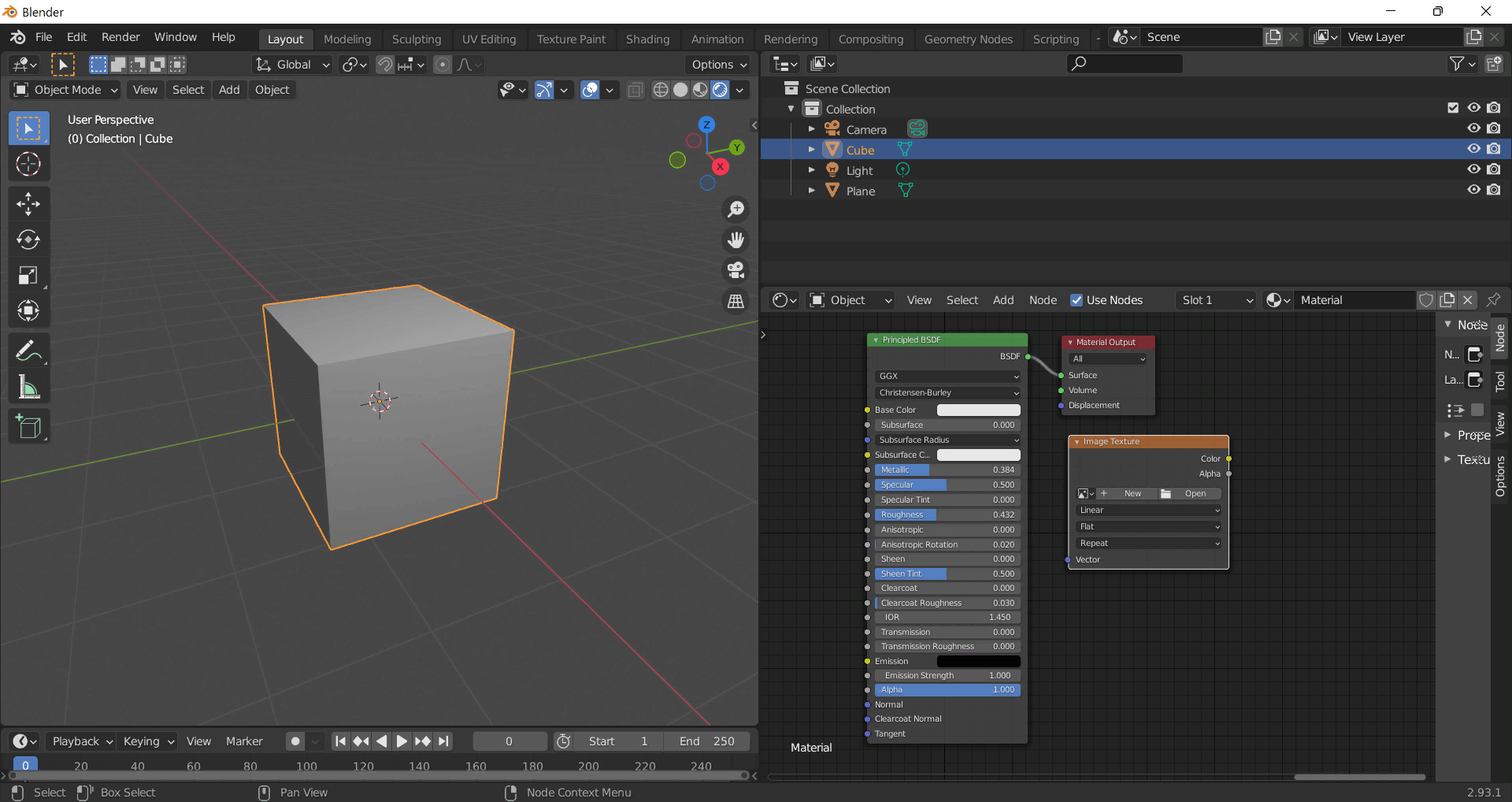
Select the required texture on your hard drive and connect Color to Base Color.